Government leaders, public sector agencies, business owners, and community residents all have a vested interest in what’s inside their local and state government budgets. However, budget documents have a tendency to be dense and difficult to read if you don’t have a background in finance.
Because these documents contain vital information, such as what services the government provides, how much funding they receive, and why these services are relevant, it’s important to prepare budget documents in a way that is accessible and understandable to a broad audience.
The Government Finance Officers Association of the United States and Canada (GFOA) recommends 28 budgeting best practices for state and local governments. Among these best practices is public engagement in the budget process, which is facilitated by another best practice, making the budget document easier to understand.
Springboarding off of the latter of these GFOA recommendations, we compiled a list of seven things state and local government budget teams can do to ensure their budget documents can be read and understood by laypeople as well as by financial experts. This transparency allows citizens to get involved in the budgeting decisions that impact them the most and creates accountability for government leaders.
7 Ways State and Local Governments Can Write Better Budget Documents
Organize documents logically
Budget documents with a logical flow are easier to understand and less prone to redundancy. The GFOA recommends organizing budget data and information into the following sections:
- Introduction and overview
- Financial structure, policy, and process
- Financial summaries
- Capital and debt
- Departmental information
- Glossary and statistical/supplemental section
Use the right amount of detail.
Although it’s important to include all relevant information in a budget document, too much detail can obfuscate important details. Keep your budget document concise by rounding numbers, minimizing text, and limiting the amount of supplemental material.
Keep the design simple.
Similarly, documents should be designed with clarity and readability in mind. Use fonts and design elements that are easy to read but engaging. Use tabs to separate content sections in hard copies of the document and bookmarks or hyperlinks from the table of contents in electronic versions.
Beach Cities Health District’s 2021-2022 budget document is an excellent example of simple but effective design. In fact, the GFOA awarded the district the Distinguished Budget Presentation Award for its commitment to clarity and for creating a budget document that can be easily understood by non-financial stakeholders.
Be consistent.
Dozens of people and multiple departments may contribute content to a budget document. Enforcing style guidelines throughout the document helps prevent inconsistency and ambiguity, creating a cohesive experience.
Call out the important parts.
Although many people want to be familiar with the contents of a budget document, few of them really need to read the document from cover to cover. Including a budget-in-brief and using data visualization to highlight important information allows stakeholders to easily understand the contents of the budget and where to find more information on a topic if they need it.
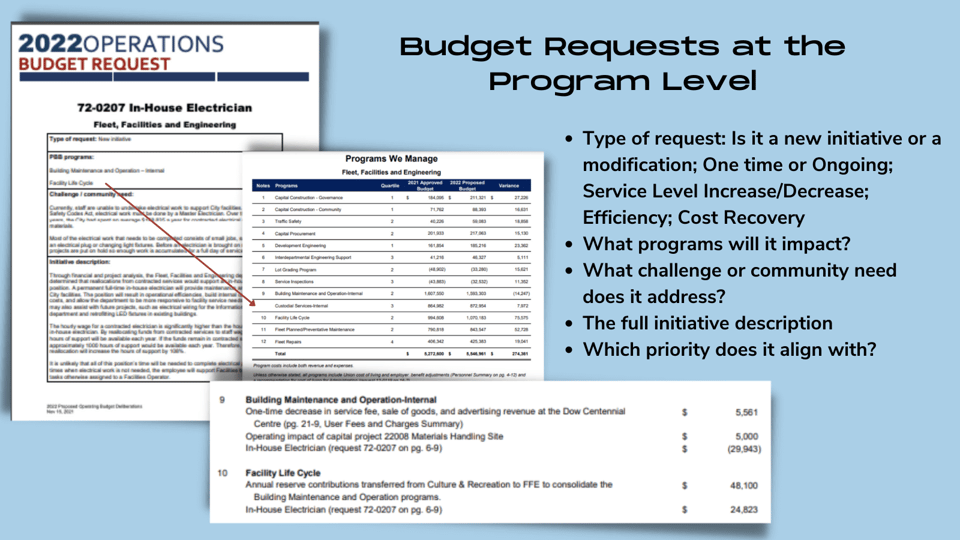
For example, Fort Saskatchewan’s budget book includes a single-page reader’s guide with a one-sentence summary of each section, as well as a supplemental budget-in-brief that provides a high-level overview of the budget using charts, graphs, and tables to illustrate key data points.
Enforce format conventions.
Formatting makes a significant impact on your budget document’s legibility. The GFOA recommends adopting a few format standards that include:
- Keeping font size, page layout, and orientation consistent throughout the document.
- Numbering pages sequentially without special characters.
- Creating identical hard copy and web versions.
For more detailed information, the group has published an official set of best practices for website posting of financial documents.
Compliance
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides standards that ensure all residents have access to government documents, including state and local government budgets.
When preparing your budget documents for the web, there are several best practices that will help make them accessible to all, including:
- Using high-contrast text.
- Adding text cues, such as “required” when using color in text.
- Adding “alt text” to images.
- Captioning videos.
- Inserting headings.
- Incorporating both keyboard and mouse navigation.
You can learn more about these and many other best practices and resources for making your website accessible on the ADA website.
If you plan to include a PDF version of your budget documents, many of the best practices apply. However, PDFs do present some additional challenges. Here are a few ways to increase PDF accessibility:
- Use structured content.
- Ensure that the PDF is tagged.
- Provide accessible links.
- Apply optical character recognition to scanned images of text.
- Enable correct language settings.
Budget Transparency Helps Align Funds with Priorities
As community needs become more complex, state and local government budgeting teams need to adopt a more agile budgeting process to ensure the highest priority programs and services receive adequate support.
Preparing your budget document based on these GFOA-inspired best practices will help you communicate clearly and concisely with all of your budgetary stakeholders—whether they’re inside city hall or out in the community.
Want to learn more about taking a priority-based approach to budgeting? Download the 2022 Impact Report now.